Best practices for using Open Politics
Open Politics is an open-source project that aims to make what is happening in politics more accessible. This guide is meant to introduce you to using the web app interface, show you what you can do with it and give you some background and best practices for using it.
It is a work in progress and we are constantly improving it. If you have any feedback or suggestions, please let us know!

Getting started with OPP
First of all you need to understand why this project exists.
Staying up to date with the world of politics is time consuming and difficult. There are countless sources reporting and even more events, issues, conflicts and elections to report about.
Time is limited, and dopamine is the currency of the 21st century. I personally know a lot of people that feel out-of-touch with what is happening. This tool is for looking something up before a discussion, to browse for worldwide news and to compare issues from around the world.
Let's start by addressing some conceptual baselines and critical information:
- The importance of news
News agencies, independent journalists and NGOs around the world are constantly documenting what is happening in politics and what people are thinking. This project does not take any perspective on what is good or bad but reflects what people are talking about, issues. Because that's what politics essentially is. - Open Source
The code, the methods and all the prompts for AI usage are documented and visible to everyone. This means that anyone can use the project, contribute to it or even build upon it. - Clear methods and reproducible answers
This project also researches the way LLMs and natural language interfacing can be responsibly done. In practice this means creating benchmarks and evaluating the reliability of AI to solve certain tasks like creating summaries, extracting sentiment and labeling information (e.g. rating between anecdotal and hot topic stories)
The tool for interactive information exploration. Scroll around the world and see what's happening
When do I use it?
While it might seem like extra work using another tool at a first glance, here are some key moments in which Open Politics will come in handy:
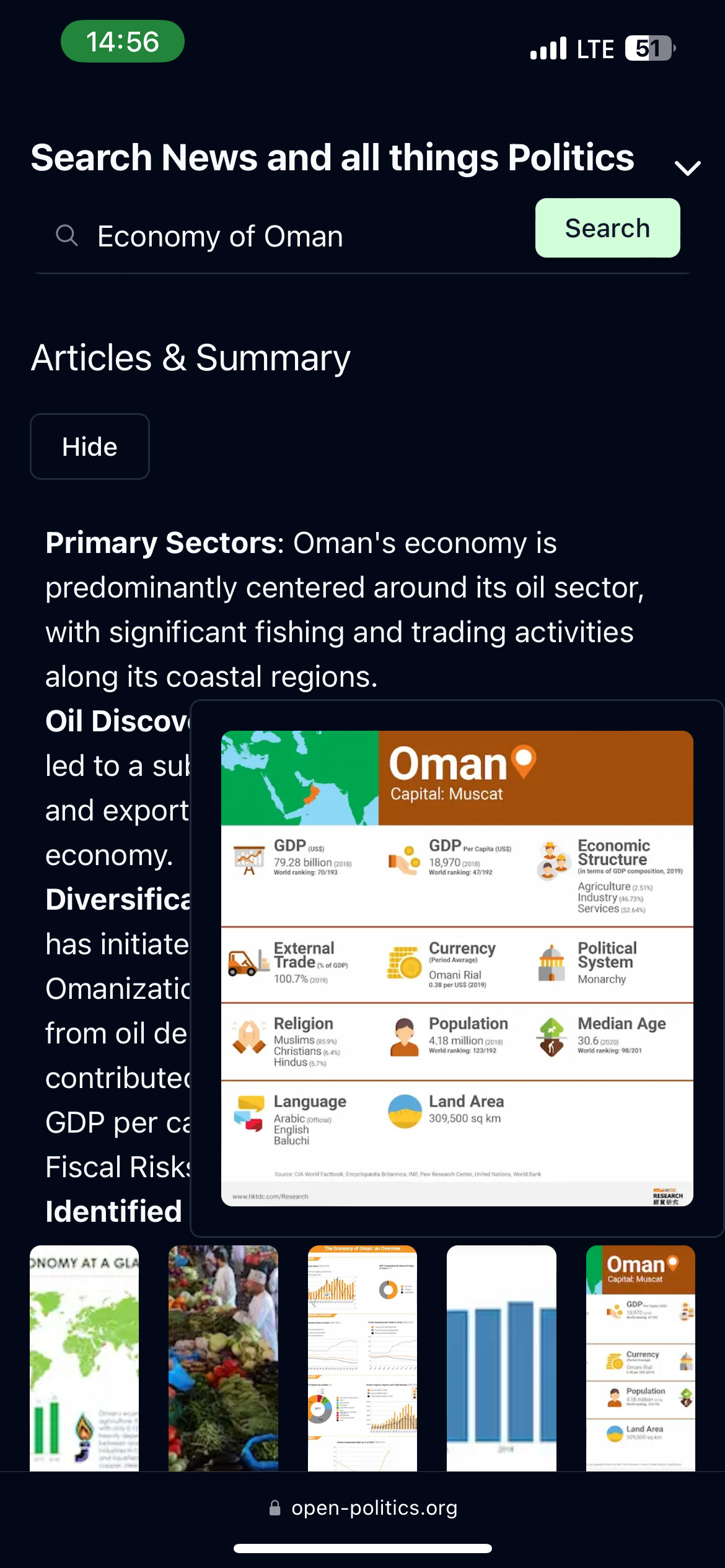
- Searching for News. Research the news for a country, a topic or issue you are interested in. One core component of the interface is the search fragment. It displays the news for your question and the extracted insights.
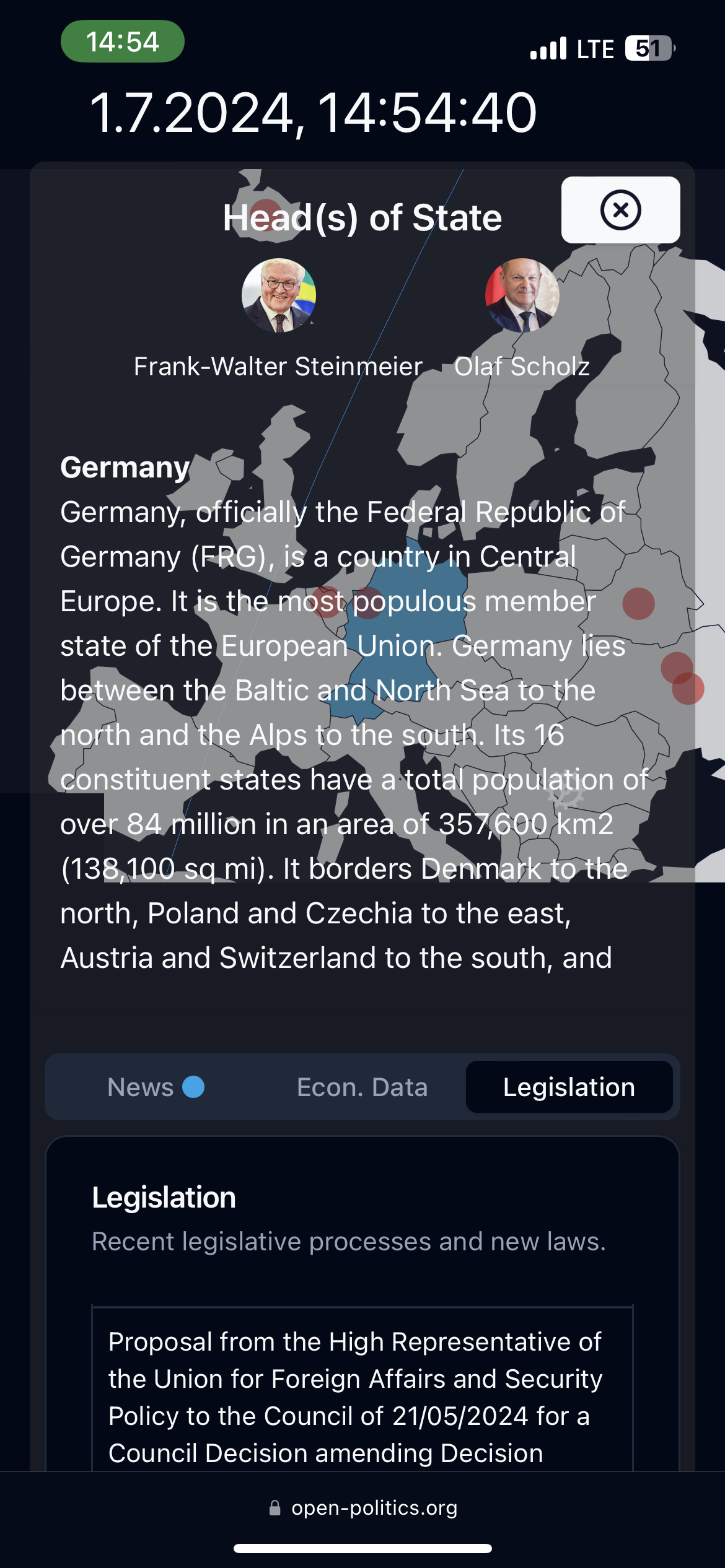
- Creating your personal focus dashboard. Create a pane with up to four of your search terms to show at once. It is essentially just multiple search fragments next to each other. You may use this to compare the economies of Malaysia and Germany or to compare between two different areas in the same country. This method of comparative analysis is at the heart of this project.
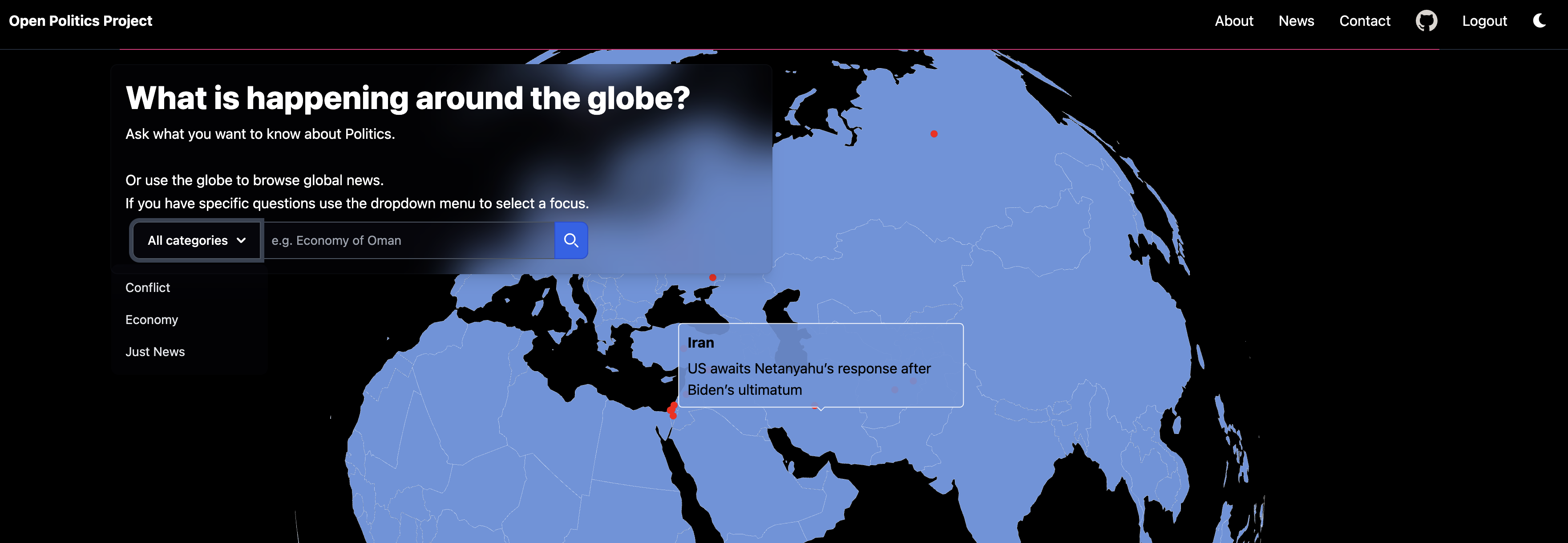
- Explorative Information. Use the Open Globe Interface and scroll through the world and see what is happening. We will give our best to make the information accessible to you and be representative of what is happening;
Think of asking somebody that is specialized in news and categorizing them. It won't give you an answer to why the world is not in peace. It will rather show what people's positions in certain issue areas are. The analysis is created around issue areas (topic), actors (and other entities) and the statements that show their position. The final component is a contextualization that compares information from sources like Wikipedia to provide historical and social contextualization for issue areas.
Let's do this step by step
This article will outline the core components of open politics search module and the open globe interface.
1. Formulate your questions

What works best is asking a question about a topic of politics and a country (or region)
2. We are extending your Search
A language model extends your questions and presses it in a certain frame. Take for example the question: What is happening in southeast asia?.
This will extend to multiple queries like this:
{
"queries": [
{
"query": "Current political events in Southeast Asia",
"category": "situation"
},
{
"query": "Economic trends in Southeast Asia",
"category": "situation"
},
{
"query": "Major political leaders in Southeast Asia",
"category": "actor"
},
{
"query": "Trade agreements in Southeast Asia",
"category": "conflict"
},
{
"query": "Foreign investment in Southeast Asia",
"category": "country"
}
]
}You can find the code that produces these search queries here.
3. Searching relevant articles
The next step is to search for articles that are relevant to your question.
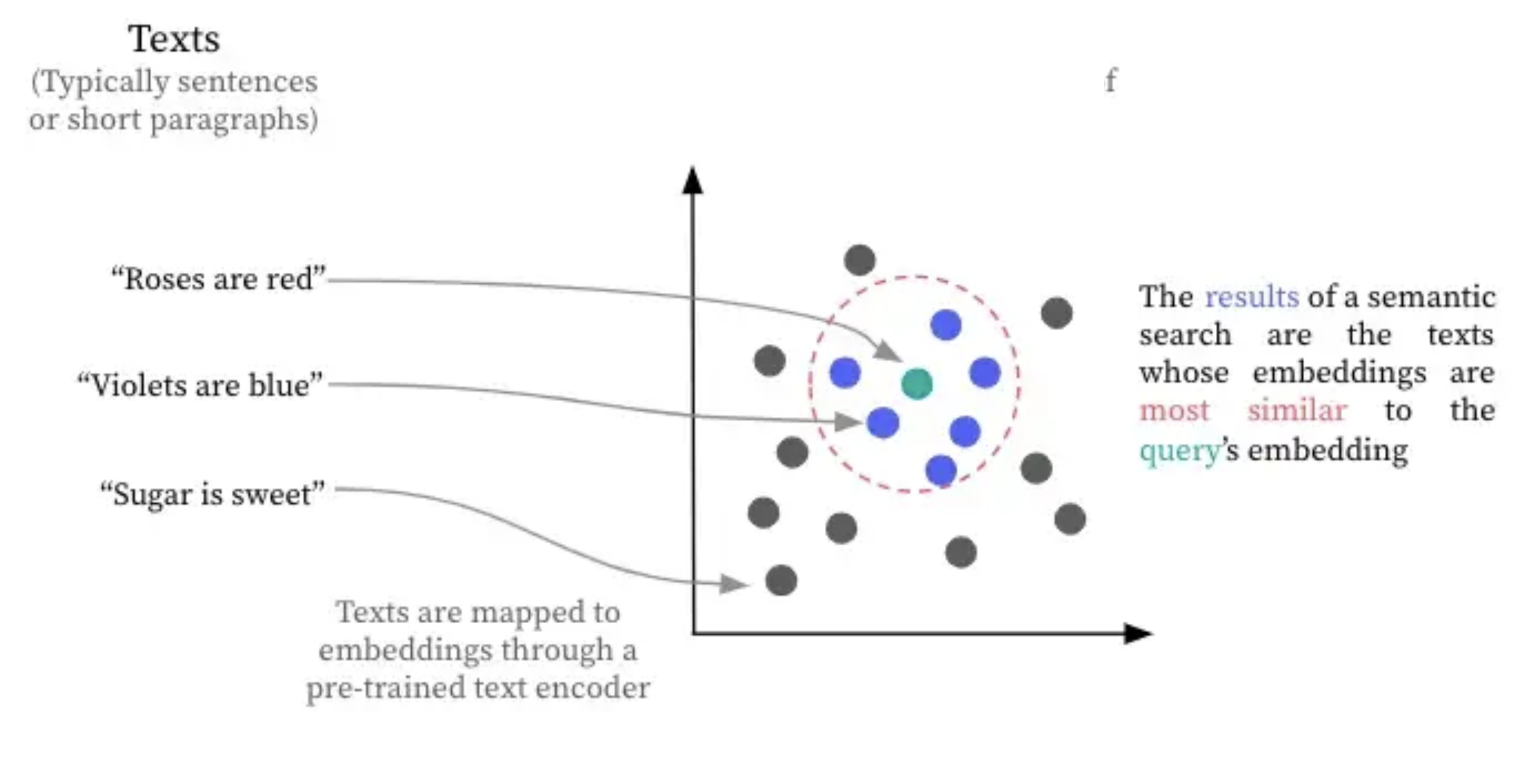
Semantic Search
The custom SSARE (Semantic Search Article Recommendation Engine) data engine scrapes and delivers news from around the world around the clock. It delivers articles by searching for text with similar semantic meaning (a newer, smarter kind of search).Entity Recognition
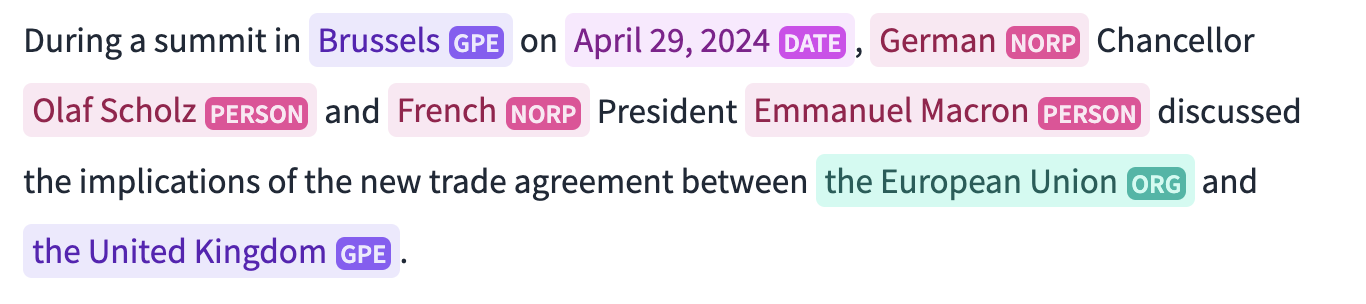
The processing concentrates mostly on Entities (like locations, institutions and organizations) and the issue areas that are found inside of news articles.
4. Extracting Issue Areas
Issue Area Extraction is done with AI. In practice this means retrieved articles (/their summaries) are fed into one prompt where the AI model is asked to extract relevant topics and return them in a structured format.
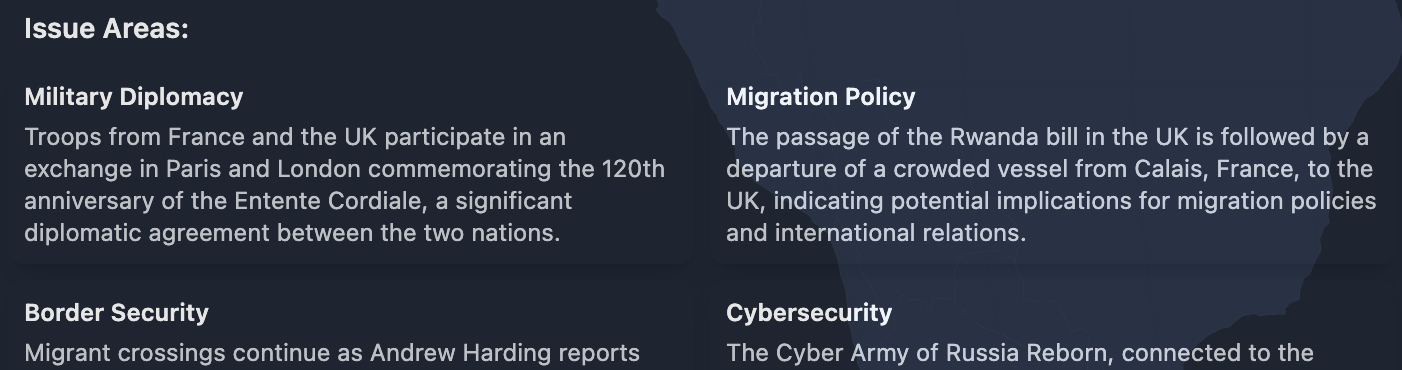
This is an old version. The issue area feature will move to the globe interface soon.
You can find the code that does this here
5. Compare
See the results of search fragments on the focus dashboard and stay up to date with what is important to you.

Expand your horizon
Global News. Important Issue Areas.
High-tech analysis.
You: up to date.
Access can be granted via waitlist or by email to engage@open-politics.org.
Join the waitlist here.